Study Notes
Episodic, Procedural and Semantic Memory
- Level:
- AS, A-Level
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
Long-Term Memory (LTM) includes any memories that are held for durations upwards of 30 seconds.
LTM can be split up into declarative memories (explicit memories that can be inspected and recalled consciously) and procedural memories (which are implicit in that we are typically unable to consciously recall them).
Declarative memory can be sub-categorised further into episodic and semantic memories, as shown in the diagram below.
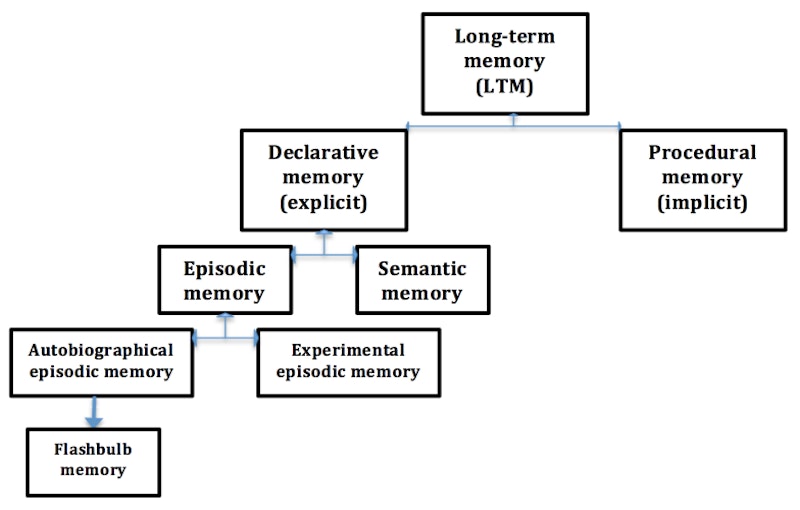
Episodic memory
Episodic memory refers to any events that can be reported from a person’s life.
This covers information such as any times, places involved – for example, when you went to the zoo with a friend last week. It is a type of ‘declarative’ memory, i.e. it can be explicitly inspected and recalled consciously. Episodic memory can be split further into autobiographical episodic memory (memories of specific episodes of one’s life) and experimental episodic memory (where learning a fact [a semantic memory, below] has been associated with memory of the specific life episode when it was learned). Flashbulb memories are detailed autobiographical episodic memories that are stored permanently in LTM when they are first learned, often because they were of emotional or historical importance in that person’s life (e.g. a birth or a death).
Semantic memory
Like episodic memory, semantic memory is also a type of ‘declarative’ (explicit, consciously recalled) memory.
However, the conscious recall here is of facts that have meaning, as opposed to the recall of past life events associated with episodic memory. For instance, recalling that you listen to music using your ears does not require knowing when or where you first learned this fact.
Procedural memory
Procedural memory describes our implicit knowledge of tasks that usually do not require conscious recall to perform them. One example would be riding a bike –you might struggle to consciously recall how to manage the task, but we can [unconsciously] perform it with relative ease.
You might also like
Capacity
Study Notes
Coding & Encoding
Study Notes
Multi-Store Model of Memory
Study Notes
Proactive and Retroactive Interference
Study Notes
Q&A from AQA: Multi-Store Model - Research for Coding, Capacity and Duration
24th February 2017
Memory: Types of Long-term Memory | AQA A-Level Psychology
Quizzes & Activities
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails