Study Notes
Biopsychology: The ‘Fight or Flight’ Response Explained
- Level:
- A-Level
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, Eduqas
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
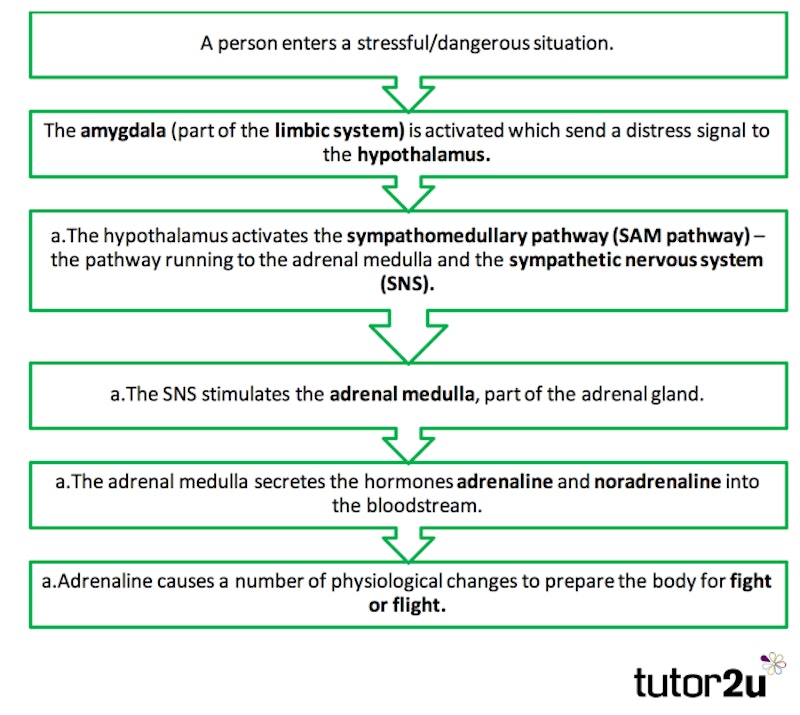
When someone enters a potentially stressful situation, the amygdala (part of the limbic system) is activated. The amygdala responds to sensory input (what we see, hear, smell, etc.) and connects sensory input with emotions associated with the fight or flight response (e.g. fear and anger).
If the situation is deemed as stressful/dangerous, the amygdala sends a distress signal to the hypothalamus, which communicates with the body through the sympathetic nervous system. If the situation requires a short-term response the sympathomedullary pathway (SAM pathway) is activated, triggering the fight or flight response.
Following the fight or flight response, the parasympathetic nervous system is activated to return the body back to its ‘normal’ resting state. Consequently, the parasympathetic nervous system slows down our heart rate and breathing rate and reduces our blood pressure. Furthermore, any functions that were previously slowed down are started again (e.g. digestion).

-

Core Topics Revision Flashcards for AQA A-Level Psychology
Printed Resource
Following the fight or flight response, the parasympathetic nervous system is activated to return the body back to its ‘normal’ resting state. Consequently, the parasympathetic nervous system slows down our heart rate and breathing rate and reduces our blood pressure. Furthermore, any functions that were previously slowed down are started again (e.g. digestion).
You might also like
The Biological Approach
Study Notes
Q&A from AQA: Biopsychology - Jet Lag & Shift Work
24th February 2017
Biopsychology: The Endocrine System - Hormones
Study Notes