Study Notes
Turnout
- Level:
- AS, A-Level
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB
Last updated 27 Aug 2017
Turnout is the percentage of eligible voters who cast a ballot in a particular election.
Electoral turnout is calculated by dividing the number of actual voters by the number of registered voters, and is usually expressed as a measure for each constituency in the election as well as for regions and the country as a whole. There are other types of turnout, including that for referendums as well as for ballots for strike action.
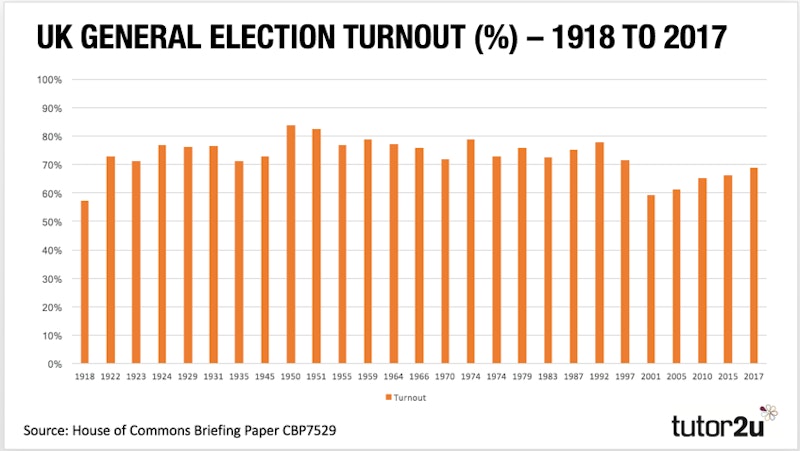
Referendum turnout has also been low, with many seeing turnout of below 45% until the Scottish Referendum which was 85%. This shows how turnout can be related to the importance of the issue being voted on.

Another way of measuring turnout is differential turnout, which is a measure of how different definable groups within society turnout for elections. For instance, in the 2010 election, turnout for 16-24 year olds was 44% and for over 65s it was 75%. This goes some way to explaining why government policy seems to be more favourable to the over 65s than to younger people.
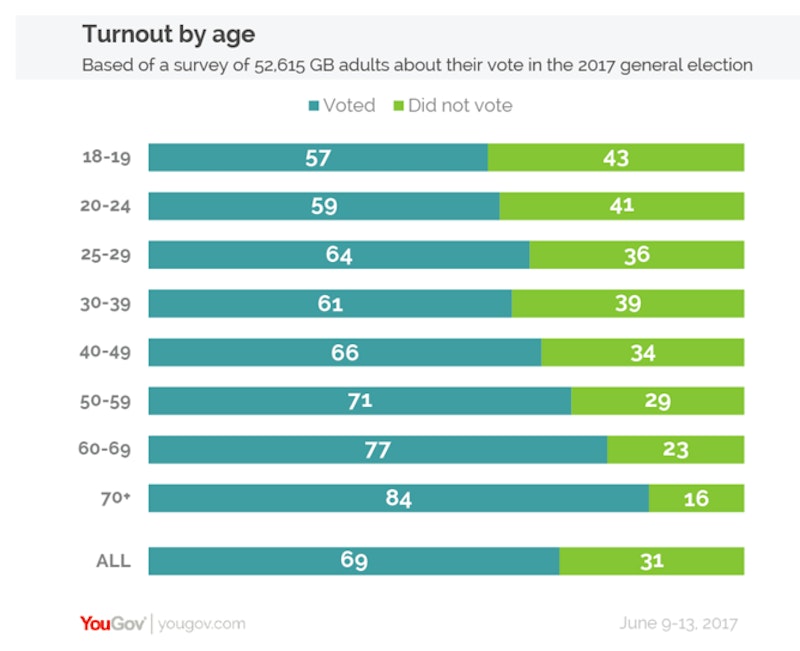
The turnout data for the June 2017 general election from YouGov (chart below) clearly indicates a much higher propensity to vote amongst older voters compared with the youngest eligible voters.
You might also like
Rational Choice Model
Study Notes
Differential Abstention
Study Notes
Compulsory Voting
Study Notes
Voter Turnout in the 2017 General Election - "Dial Up" activity
Quizzes & Activities

