Explanations
Alternative Vote Explained
7th November 2016
Next in the Electoral Systems series is that of the Alternative Vote. This is the electoral system that Britain held a referendum on in 2011.
Read the first instalment of this series, First Past The Post Explained, if you haven't already.
The Alternative Vote:
This electoral system is occasionally called Instant Run Off Voting. Just like the first past the post it seeks to elect members from single seat constituencies or wards. However, unlike FPTP, AV asks electors to rank their candidates in order of preference.
Once the votes are counted, the results are analysed. Should one candidate hold a majority of the votes they are elected. If not then the worst performing candidate has the second choices redistributed. As soon as one candidate has a majority they are elected. Irish Presidential and Australian Parliamentary elections use the Alternative Vote.
The 2015 Election Under AV
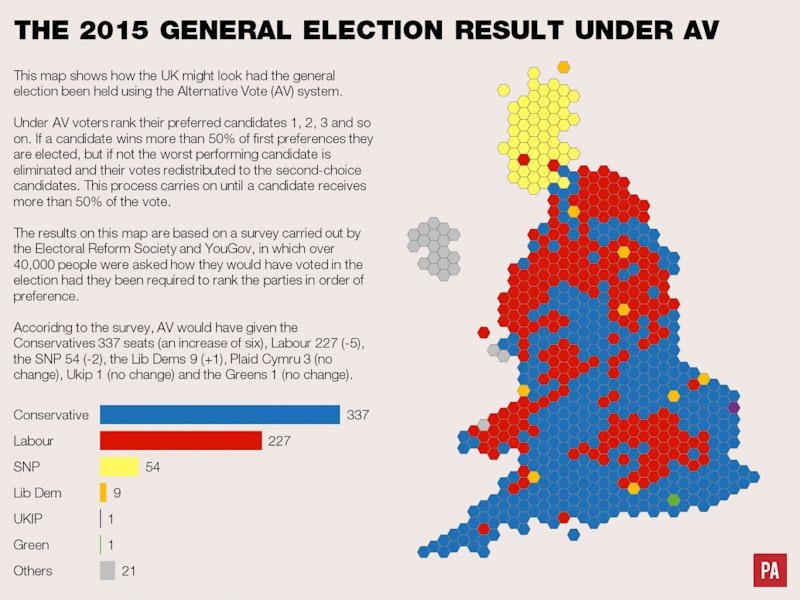
Had the 2015 General Election been run under AV the results would have been slightly different to the FPTP results.
- Conservatives: 337
- Labour: 227
- Lib Dems: 9
- SNP: 54
- UKIP: 1
- Green: 1
- Others: 21
You might also like
Labour leadership election - How the Alternative vote works
7th September 2015

The difference between the UK, GB and England
28th January 2016
Petty, Mean, and Deliciously Rude, yet still better than US Politics
26th February 2016
Edexcel A-Level Politics Bumper Revision Quiz for Component 1
Quizzes & Activities
Nigel Farage has quit the leadership of Reform UK
9th March 2021
First past the post not so stable
22nd March 2024
Green Party: minor party case study
14th June 2024