Study Notes
Introduction to Carbon and Carbon Stores
- Level:
- AS, A-Level
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
Carbon is an essential element to all living things on earth – plants and animals, surface and marine. It also plays a major role in regulating global climate, particularly temperature and in determining the acidity of rain, rivers and oceans.
Carbon cycles, like water cycles, should be thought of as a system. There are inputs, stores, fluxes/flows and outputs that transfer carbon from one environment to another and cause stores to be depleted, or accumulate.
Carbon stores (reservoirs): location
The main stores of carbon are located in, and transferred between the:
- atmosphere: mainly as carbon dioxide CO2 but also shorter-lived methane CH4
- biosphere: all living organisms are composed of carbon occupying various environments
- cryosphere: the frozen ground of tundra and arctic regions containing plant material
- pedosphere: soil contains much organic carbon and the remains of dead plants & animals
- lithosphere: many of the rocks of the earth’s crust contain carbon, such as chalk/limestone (calcium carbonate)
- hydrosphere: the oceans contain much dissolved CO2 as well as marine
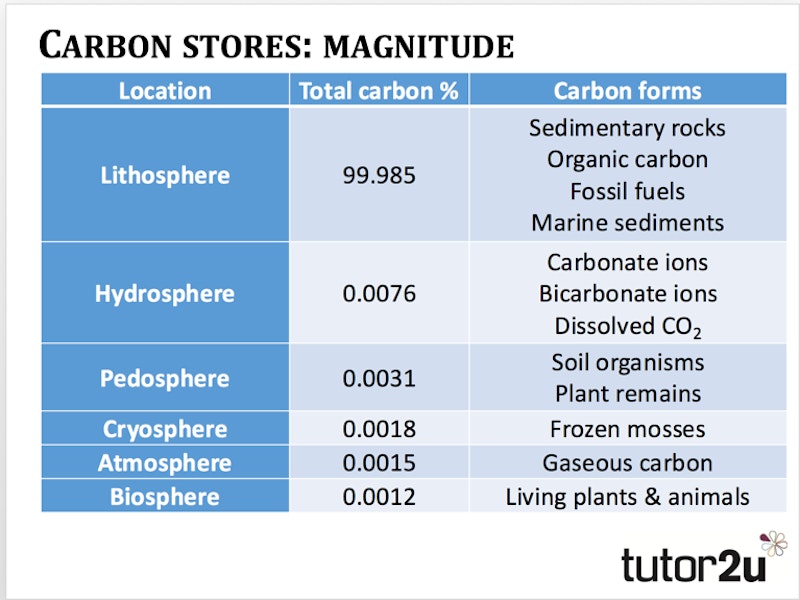
Carbon stores: magnitude
You might also like
Slow carbon cycle
Study Notes

Blue whale poo: stimulating carbon sequestration in southern oceans
29th November 2018
The lessening role of soil in the carbon cycle
25th March 2021

What’s the Carbon Footprint of Qatar 2022?
21st November 2022

COP15 - "best and last chance" to halt and reverse the decline of nature
15th December 2022