Study Notes
X-Inefficiency
- Level:
- A-Level
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
X-inefficiency happens when a lack of effective / real competition in a market or industry means that average costs are higher than they would be with competition
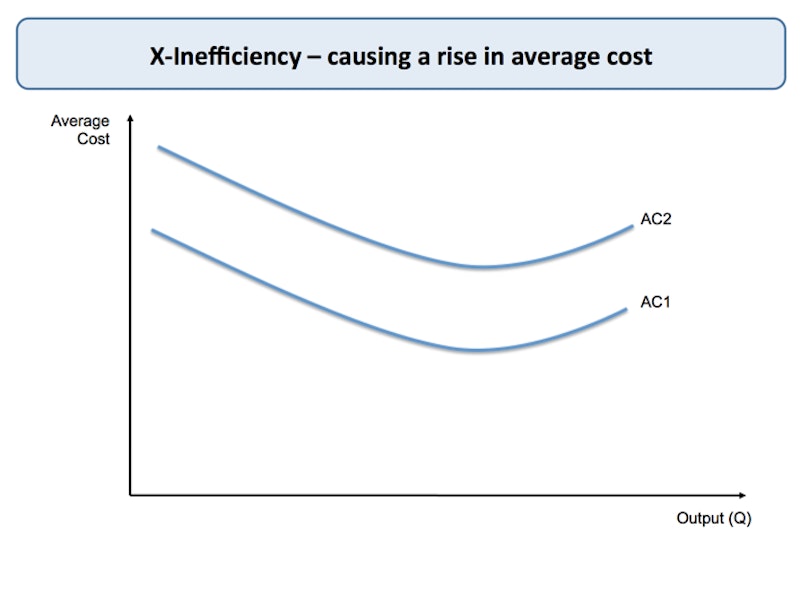
Some common examples of x-inefficient behaviour include businesses happy with satisficing profits, permitting a degree of organisational slack, and rising average costs of labour as wages rise or over-manning occurs
The added complexity of businesses and senior and middle management with other aims such as the perks that come with high status jobs can also bring about higher costs.
Patents may lead to x-inefficiency, patents are legal barriers which prevent copying of names or concepts by rival firms these act as a barrier to entry meaning that new firms cannot enter/force existing firms to cut their prices or costs – there is no need for existing firms to cut costs
You might also like
Economic Efficiency Revision Quiz
Quizzes & Activities
Production Possibility Frontier
Topic Videos
Monopoly and Welfare: Over-pricing for school uniforms
16th October 2015
Evaluating Monopoly (AS Micro)
Topic Videos
Monopolistic Markets (MCQ Revision Questions)
Practice Exam Questions
Barriers to Entry (Quizlet Revision Activity)
Quizzes & Activities
Market Structures (Revision Quizlet Activity)
Quizzes & Activities
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails