Study Notes
What is disinflation?
- Level:
- AS, A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 26 Jul 2023
Disinflation refers to a decrease in the rate of inflation, meaning that the overall price level is still increasing, but at a slower pace than before. It is important to note that disinflation is different from deflation, which refers to a sustained decrease in the overall price level.
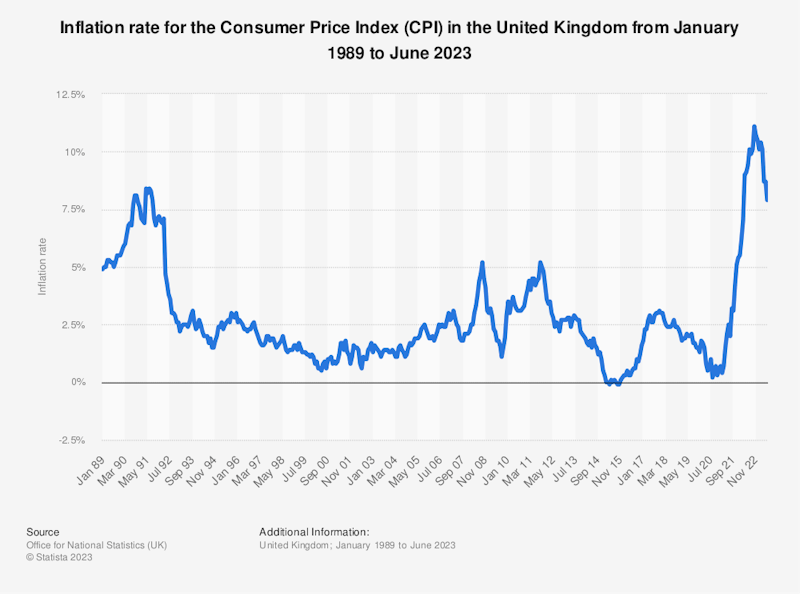
Here are a couple of numerical examples to illustrate disinflation:
Example 1: Let's consider a hypothetical economy where the annual inflation rate was 6% in the previous year. However, in the current year, the inflation rate drops to 2%. This decrease in the inflation rate indicates disinflation. While prices are still rising, the pace of the price increases has slowed down.
Example 2: In another scenario, let's say an economy experienced an inflation rate of 10% in the previous year. In the current year, the inflation rate falls to 5%. Again, this decrease in the rate of inflation represents disinflation. Prices are still increasing, but at a reduced rate compared to the previous year.
In both examples, the economy is experiencing disinflation because the inflation rate is declining, indicating a slowdown in the rate of price increases.
Disinflation can occur for various reasons, such as tighter monetary policy (higher interest rates), reduced aggregate demand, lower commodity prices, or increased labour productivity.
Disinflation is often seen as a positive development because it can contribute to price stability and make it easier for individuals and businesses to plan their economic activities.
However, if disinflation turns into deflation, it can have negative consequences such as a decrease in consumer spending, increased debt burdens, and lower economic growth.
How is disinflation different to deflation?
- Disinflation is a decrease in the rate of inflation, meaning prices are still rising, but at a slower pace. It's a milder form of inflation.
- Deflation is an outright decrease in the general price level, with prices falling over time. It represents a negative inflation rate.
You might also like

Low or zero inflation is normal: competition keeps it that way
24th September 2014
Nominal and Real Interest Rates
Topic Videos
Prospects for the Greek Economy
Study Notes
Greek Economy: Current Issues (2017)
Topic Videos

Alexa joins the Consumer Price Index!
11th March 2019

UK Economy Update: Inflation Rate Drops to 8.7%
24th May 2023
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails