Exam Support
Trade Unions and Real Wages (Chain of Analysis)
- Level:
- AS, A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 20 May 2018
Here is an example of a chain of analysis on how a fall in trade union membership might affect real wages and employment in the labour market.
Evaluate the possible effects on the UK labour market of a decrease in trade union membershi
Chain of reasoning Point 1
One effect of falling trade union membership is that the reduced collective bargaining power of workers may lead to lower real wages
This is because trade unions lobby on behalf of their members with employers for better real pay and conditions.
If unions are less powerful, an employer with monopsony power might be able to take people on by offering reduced terms.
They may pay workers a going wage rate less than would be the case if wages were set in competitive labour markets
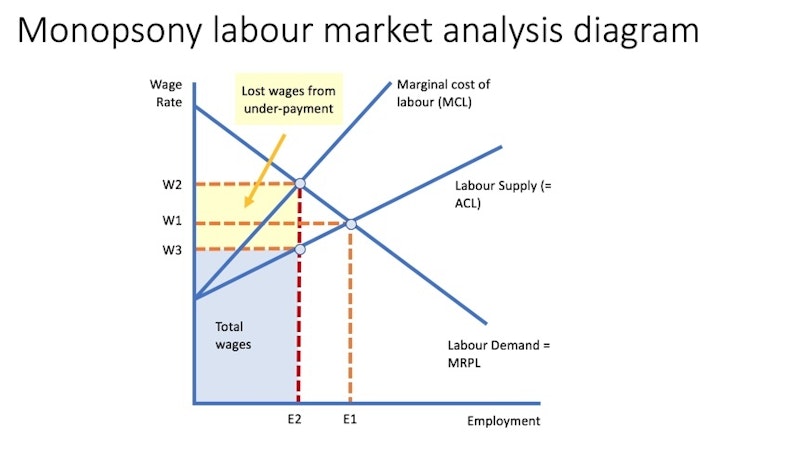
This is shown in my monopsony diagram where profit maximising employment level is E2 & MRPL = W2 but the wage on offer is only W3
Wage W3 is below the value of marginal revenue product of labour and suggests workers without trade union protection might be exploited
You might also like
Supply-Side Reforms (Labour Markets)
Study Notes
Trade Unions in the UK (Labour Markets)
Topic Videos
Zero Hours Contracts (Labour Markets)
Study Notes
Minimum Wage - Evaluation Phrases in Action
Study Notes
Amazon a 'phenomenon' of 21st century retail
7th March 2019
California legislates to protect gig economy workers
12th September 2019

Heathrow posts operating loss of nearly £1 million a day
29th July 2022
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails