Study Notes
Revenue Curves in Competitive Markets
- Level:
- A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 21 Mar 2021
In a perfectly competitive market, total revenue (TR) is a diagonal straight line passing through the origin. Market demand and supply determine the price and each firm is a price taker.
Thus, average revenue is constant
Thus, average revenue – marginal revenue at the prevailing market price
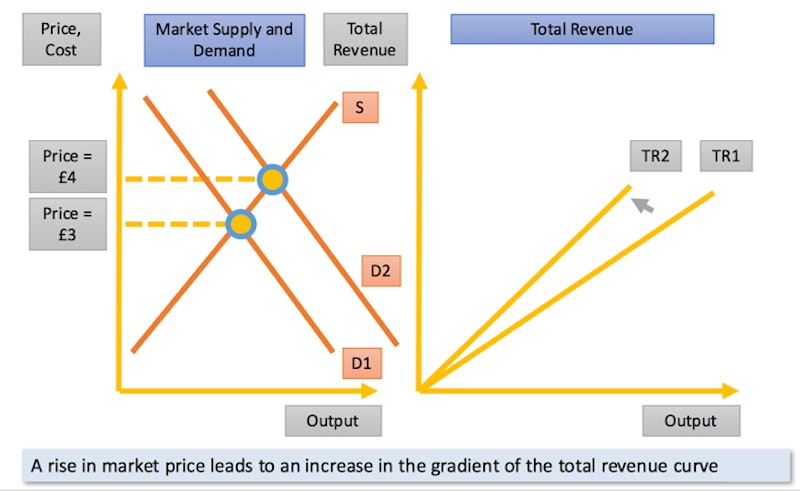
Changes in the market price will bring about a change in the gradient of the total revenue curve for firm in a perfectly competitive market
TR when there is a rise in market price
A rise in market price leads to an increase in the gradient of the total revenue curve
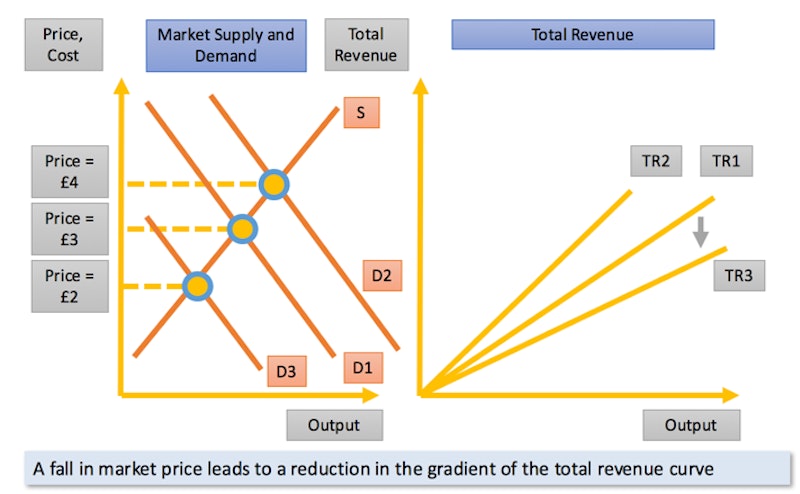
TR when there is a fall in market price
A fall in market price leads to a reduction in the gradient of the total revenue curve
You might also like
Contestable Markets
Topic Videos
Revenue in Perfectly Competitive Markets
Topic Videos
Business objectives of discount supermarkets
6th October 2017
Key Micro Diagrams (Market Structures)
Topic Videos
Business Revenues: Contextual examples from 2020
Topic Videos
3.4.2 Perfect Competition (Edexcel)
Study Notes

The Renaissance of English Wine: An Economic Perspective
5th August 2024
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails