Topic Videos
Price Volatility in the Coffee Market
- Level:
- AS, A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 14 Jan 2018
This revision video looks at some of the causes of price volatility in the international coffee market. Market prices tend to be volatile when demand and supply are inelastic in response to price changes in the short run and when there are unexpected fluctuations in the conditions of demand and supply.
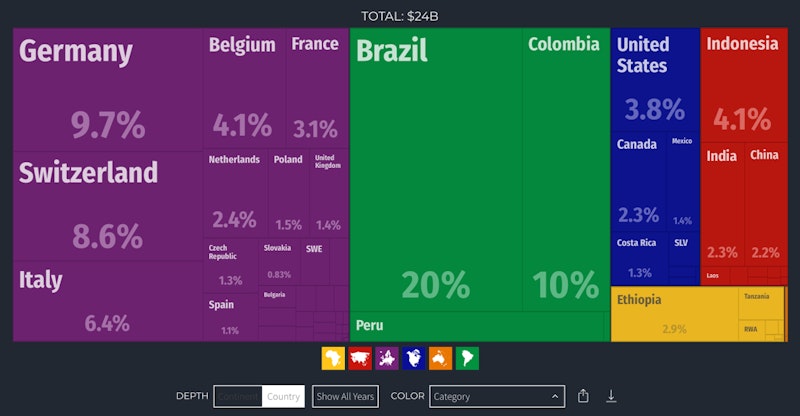
Coffee is the 117th most traded product in the global economy and the 948th most complex product according to the Product Complexity Index. But the importance of coffee is hard to understate. Coffee is grown in more than 60 countries and raw and processed coffee beans are the most traded commodity in the world after oil. 25 million families worldwide make a living from coffee production although the bulk of profits flow not to producers but to businesses who roast the beans and turn it into higher value-added products. Brazil is by far the largest global producer, followed by Vietnam and Colombia.
Demand
Demand factors affecting the price of coffee include:
- (i) Growing demand in emerging nations as per capita incomes rise - consumption of coffee in China has doubled in the last five years
- (ii) Prices of substitutes for coffee such as tea and cocoa
Supply
Supply factors affecting the price of coffee include:
- Climatic conditions e.g. the impact of el Nino
- Existing levels of coffee stocks (inventories)
- The number of countries producing coffee
- Productivity and investment in coffee production in the major coffee farming nations
Falling stock levels put upward pressure on price – prices seem set to rise in 2018 partly because rising demand has reduced existing stock levels. Scarcity drives prices higher.
Long term threats to coffee supply
There is growing consensus among experts that climate change will severely affect coffee crops over coming years
Climate change is threatening the land used to grow coffee - a rising land surface will not be suitable for arable farming
Coffee provides a livelihood for close to 15 million Ethiopians, 16% of the population. Climate change is a major threat to the resilience of their economy.
Key economic issues to consider
Causes of price volatility in markets
Micro consequences of volatility e.g. for farm incomes, profits, employment and investment
Macro consequences of volatility e.g. for exports (balance of payments), GDP, tax revenues, prospects of poverty reduction
How can price volatility be moderated?
- Buffer Stock Schemes
- Innovation in farming
- Investment to tackle long-term challenges of climate change
You might also like
Understanding the Economic Cycle
Study Notes
Cocoa Market
Study Notes
Stellios opens his easyFoodstore with 25p offers!
2nd February 2016
The Importance of Trade in Raw Materials
9th February 2017
Evaluating Subsidies (Online Lesson)
Online Lessons

Will the global supply chain process lead to stagflation?
22nd September 2021
Growth and Development Profile - Zambia
Topic Videos
