Topic Videos
Explaining Price Elasticity of Demand and Total Revenue
- Level:
- AS, A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 20 Dec 2021
In this video we explore the relationship between the coefficient of price elasticity of demand and the effect that price changes have on total revenues.
When the coefficient of PED < 1, then a rise in price will increase total revenue. For example, if PED = -0.3, this means demand is price inelastic
When the coefficient of PED > 1, then a price fall will increase total revenue. For example, if PED = -2.5, this means demand is price elastic
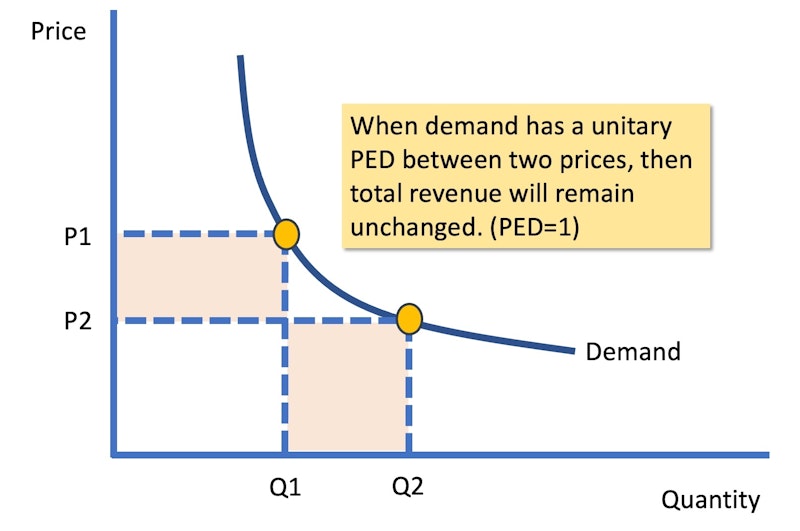
When the coefficient of PED = 1, then demand is unitary elastic. This means a price change will leave total revenue unchanged
When demand is price inelastic, consumers are less sensitive to the price being charged. They have a lot of consumer surplus which businesses can possibly extract into extra revenue – perhaps as a result of price discrimination.


You might also like

Coca Cola enters the milk market
26th November 2014
Coffee Market
Study Notes

Fermenting Nicely - The Rise of Microbreweries
31st August 2015

Is surge pricing heading to UK supermarkets?
2nd July 2017
Business Economics - "Keepy Uppy" revision activity
Quizzes & Activities
Marginal Utility and the Demand Curve
Topic Videos
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails