Topic Videos
Pareto Efficiency and Pareto Improvements
- Level:
- AS, A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 21 Nov 2019
The concept of Pareto efficiency and Pareto improvements in welfare are covered in this short topic video.
What is Pareto efficiency?
- In neo-classical economics, a Pareto efficient outcome is an action that harms no one and helps at least one person.
- A situation is Pareto efficient if the only way to make one person better off is to make another person worse off.
- The production possibility curve can be used to illustrate the concept of Pareto efficiency and Pareto improvements in welfare
Pareto efficiency and the PPF
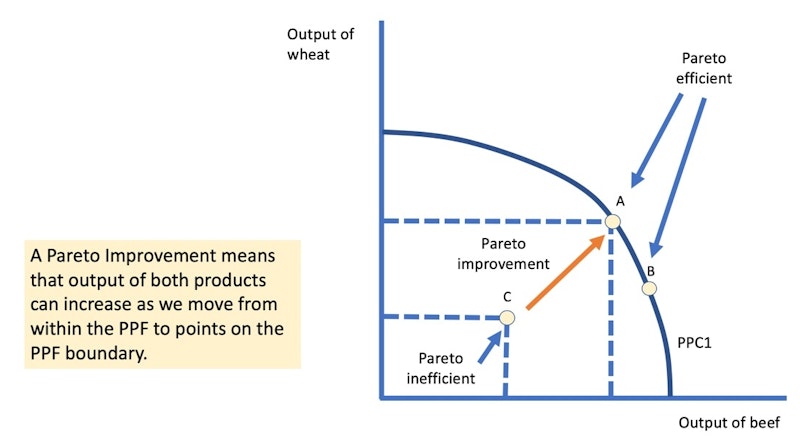
Pareto efficiency will occur on points that lie on a production possibility frontier / curve
When an economy is operating on a production possibility frontier, it is not possible to increase output of goods without reducing output of services
When an economy lies well within the PPF boundary, there is an inefficient use of resources or under-utilization of resources
Here it becomes possible for output of two goods or services to increase at the same time
Points that lie within the PPF show an inefficient or under-utilization of resources – this is Pareto inefficient.

A Pareto Improvement means that output of both products can increase as we move from within the PPF to points on the PPF boundary.
Pareto efficiency and equity
- An outcome may be a Pareto improvement, but it doesn’t always mean this is a satisfactory outcome or fair (i.e. equitable)
- There could still be inequality after a Pareto improvement
- We need to see which groups / people benefit from increased output of goods and services i.e. consider social welfare
- Showing on a diagram a Pareto improvement involves no judgement about the equality of final distribution or overall social welfare.
You might also like
Innovation and Invention in Markets
Study Notes
Perfect Competition - Economic Efficiency
Study Notes
Economic Efficiency Revision Quiz
Quizzes & Activities
Advantages and Disadvantages of Monopoly Power
Topic Videos
A* Evaluation on Business Conduct and Efficiency
Topic Videos
Market Failure - Match Up Knowledge Retrieval Activity
Quizzes & Activities
4.1.5.10 Static and Dynamic Efficiency (AQA A Level Economics Teaching Powerpoint)
Teaching PowerPoints
3.4.1 Efficiency (Edexcel)
Study Notes
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails