Study Notes
Explaining Price and Output in a non-collusive Oligopoly
- Level:
- AS, A-Level
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
An oligopoly is an imperfectly competitive industry where there is a high level of market concentration
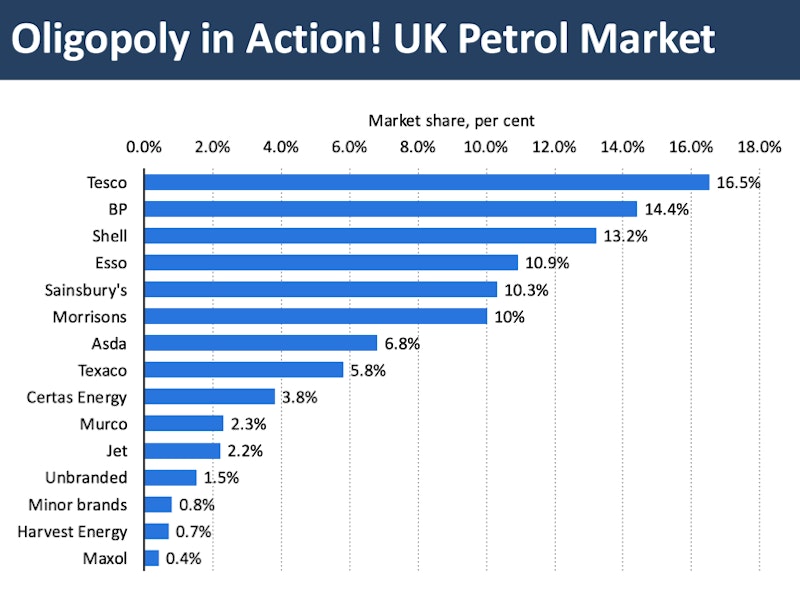
Examples of markets that can be described as oligopolies include the markets for petrol in the UK, soft drinks producers and the main high street banks. In the global market for sports footwear – 60% is held by Nike and Adidas
- Oligopoly is best defined by the actual conduct (or behaviour) of firms within a market
- The concentration ratio measures the extent to which a market or industry is dominated by a few leading firms.
- A rule of thumb is that an oligopoly exists when the top five firms in the market account for more than 60% of total market sales

Britain's cinema market is dominated by Odeon, Vue and Cineworld - the latter being the only operator listed on the London Stock Exchange. Together, they account for about 70% of the UK's screens
What are the main characteristics of an oligopoly?
An oligopoly usually exhibits the following features:
- Product branding: Each firm in the market is selling a branded product which is built and protected by heavy spending on advertising and marketing
- Entry barriers: Entry barriers maintain supernormal profits for the dominant / established firms. It is possible for many smaller firms to operate on the periphery of an oligopolistic market, but none of them is large enough to have any significant effect on prices and output
- Inter-dependent decision-making: Inter-dependence means that firms must take into account the likely reactions of their rivals to any change in price, output or forms of non-price competition
- Non-price competition: Non-price competition is a consistent and crucial feature of the competitive strategies of oligopolistic firms especially when they are growing or defending market share
Key revision points
- There is no single theory of price and output under oligopoly.
- If a price war breaks out, oligopolists may produce and price much as a highly competitive industry would; at other times they act like a pure monopoly.

You might also like
Shut Down Price (Short Run)
Study Notes

Tobacco firms launch a legal challenge against plain packaging
10th December 2015
Fantasy Economics for AS and A2 students!
14th April 2016

Short Videos on Price Fixing
1st February 2017
Price and Non-Price Competition in Oligopoly
Topic Videos
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails