Study Notes
Monopsony Power in the Labour Market
- Level:
- A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 13 Apr 2018
A monopsony occurs when there is a sole or a dominant employer in a labour market.

This means that the employer has buying power over their potential employees. This gives them wage-setting power in the industry labour market.
Monopsony is a potential cause of labour market failure. For a monopsony employer, the supply curve of labour equals the average cost of labour. The monopsony employer will have to bid up wages in order to attract new workers.
But the wage they pay will not necessarily be equal to the true marginal revenue product of people they have employed
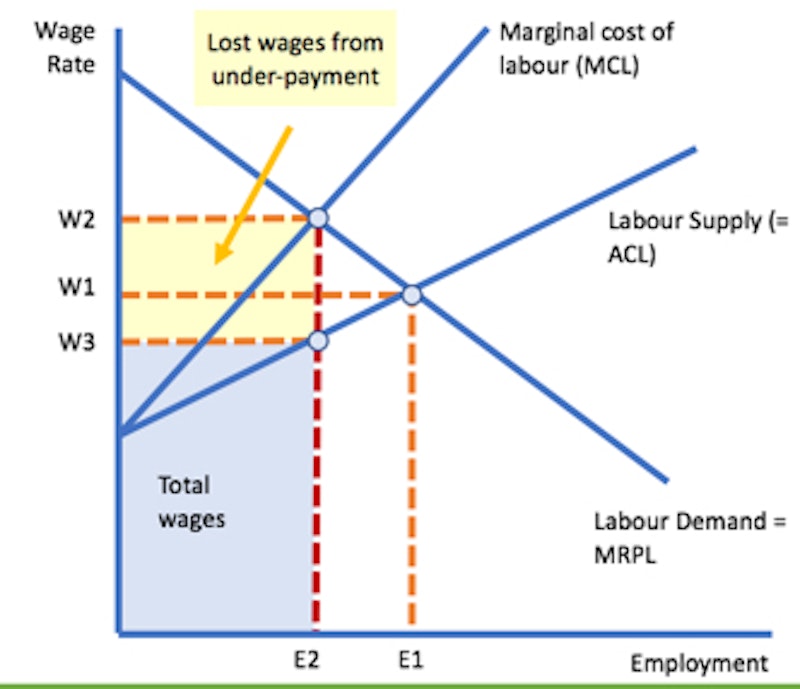
Analysis of monopsony power when setting wages
Profit maximising employment level is where MCL=MRPL i.e. E2 number of people are employed
Their marginal revenue product is valued at W2
Monopsony power of the employer allows them to pay a wage rate W3

Monopsony employer can use their buying power to pay a wage lower than the value of the marginal revenue product of workers employed at E2
Monopsony power can therefore lead to exploitation of employed workers
You might also like

Economics of Falling Milk Prices
11th August 2015

Must Watch Revision Videos on Labour Markets
1st June 2018
Zero Hours Contracts (Labour Markets)
Study Notes

Labour Markets - Where have all the workers gone?
2nd August 2021

UK Economy - What can be done to reduce economic inactivity?
23rd October 2022

Construction Crunch: Why the UK Can't Meet Its Housing Targets
14th December 2024
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails