Study Notes
How Markets Work - Introductory Demand Concepts
- Level:
- AS, A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 24 Jan 2019
Here are some core revision notes covering an introduction to the operation of markets and the working of the price mechanism.
What is meant by?
COMPLEMENT
Goods and services that are used and bought together e.g. milk and sugar, pancakes and lemon, printers and paper
CONDITIONS OF DEMAND
Any factor other than price which might lead to an outward / inward shift of demand for a product e.g. interest rates, income
DEMAND
The amount that consumers are willing and able to purchase of a good/service at a given price in a given time period
MARGINAL UTILITY
The change in total satisfaction from consuming one extra unit of a product
PROFIT
The difference between total revenue and total cost, profit is a reward to risk-taking by an entrepreneur
RATIONAL BEHAVIOUR
Rationality means using all the available information to make optimal choices and also learning and responding to mistakes.
REAL INCOME
Money income adjusted for price changes – measures the quantity of goods and services that a given budget can buy
SUBSTITUTE GOOD
A good in competitive demand with another product e.g. two brands of beer, Netflix versus Amazon Prime
UNRELATED GOODS
Where a change in the price of one product (e.g. cheese) has not impact whatsoever on the demand for another product (e.g. foreign holidays)
WILLINGNESS TO PAY
Otherwise known as effective demand, i.e. when demand from a consumer is backed by an ability to pay
Give me 5 reasons why demand may increase (i.e. the demand curve shifts to the right)
- 1. Increasing income (for normal goods)
- 2. Decreasing income (for inferior goods)
- 3. Rising price of substitutes
- 4. Falling price of complements
- 5. Effective advertising
Give me 5 reasons why demand may decrease (i.e. the demand curve shifts to the left)
- 1. Change in consumer tastes and preferences away from the product
- 2. Rise in interest rates leading to a fall in demand for products bought on credit
- 3. Expected fall in prices leading consumers to delay their purchases
- 4. A rise in unemployment during a recession
- 5. A rise (appreciation) in the exchange rate which makes import (substitutes) cheaper
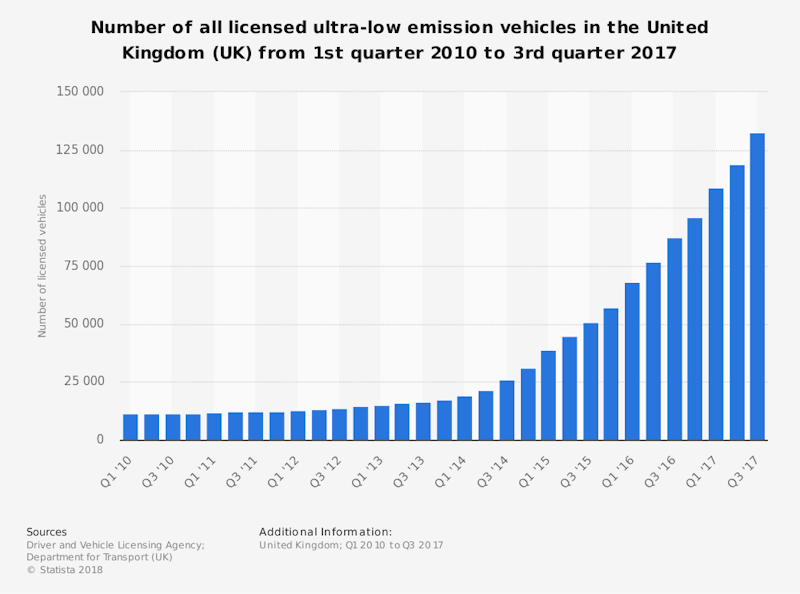
Identify 3 factors behind the growth of market demand for low-emission cars in the UK:
- Government grants for plug-in hybrid cars (now ended)
- Expansion of network of charging stations and falling prices for recharging
- Higher fuel taxes on petrol and diesel vehicles
Identify 2 other (related) products whose demand will be impacted by the data in the chart:
- Demand for electric vehicle charging stations
- Demand for solar panels for households to charge their cars at home
Identify 1 policy a government could use to stimulate demand for ultra-low emission cars:
- Increasing the fuel duty on all petrol/diesel vehicles
You might also like
How Markets Work - The Price Mechanism
Teaching PowerPoints
Thirst for Coffee Brews Chronic Supply Shortage
9th February 2016
Consumer sovereignty and the changing face of Swiss chocolate
13th April 2017
Farm Subsidies (Revision Essay Plan)
Practice Exam Questions
Key Micro Diagrams (Market Failure)
Topic Videos
Markets in Action - Crude Oil Prices
Topic Videos

Supply and demand in action - why the price of milk has soared in the UK
20th February 2023
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails