Topic Videos
Exceptions to the Law of Demand Explained
- Level:
- AS, A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 23 Dec 2021
In this video we look at two possible exceptions to the law of demand, namely Giffen Goods and Veblen Goods.
There are possible exceptions to the law of demand. Giffen goods are highly inferior products with few substitutes. Veblen goods are high-luxury products linked strongly to buyers gaining satisfaction from conspicuous consumption. Veblen goods are more likely in reality than Giffen goods.
What is the law of demand?
The law of demand states that, other factors remaining constant, the quantity bought of a good or service varies inversely with the price charged.
Lower prices cause an expansion of demand; higher prices cause demand to contract.
Broad Explanation of the Law of Demand
For normal goods, quantity demanded expands as prices fall because:
- There is positive substitution effect on demand from people switching from relatively cheaper competing products in the market
- There is a positive real income effect on demand – lower prices cause real incomes of consumers to increase, and normal goods have a positive income elasticity of demand
Thus, when prices drop, we see an expansion along the demand curve
What is a Giffen Good?
A Giffen good is where a higher price causes an increase in demand. This is due to the income effect of the higher price outweighing the substitution effect.
What is a Veblen Good?
A Veblen good is a good where demand rises as price rises because people enjoy the status that comes from conspicuous consumption of high-quality luxury products.
Thorstein Veblen coined the term conspicuous consumption - where people gain satisfaction from being seen to be consuming high-priced, luxury goods and services such as designer jewelry and expensive cars.
Positional goods
Positional goods are goods valued only byhow they are distributed among the population. They have strong desirability as a status symbol, which usually results in them greatly exceeding the value of comparable goods. Higher prices ration who can afford to buy and consume them.
Why might demand increase when the price of a Giffen Good rises?
- Giffen Goods have few close substitutes and a highly negative income elasticity of demand
- When price rises, the substitution effect causing a fall in demand is weak because of the absence of suitable substitutes
- When prices rise, real incomes fall but demand rises because income elasticity of demand is negative, so consumers buy more
- Overall, a higher price can cause demand to rise rather than contract.
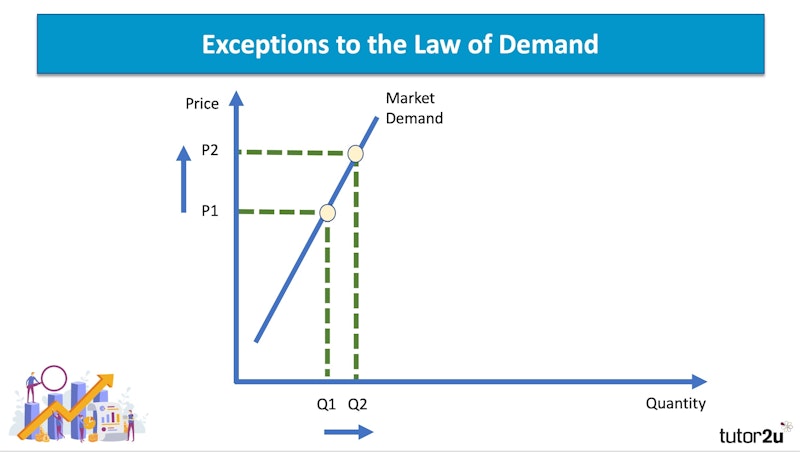
When buyers of a product expect further price rises, then this can lead to an increase in quantity demanded. Certainproducts have an element of speculative demand – although this can be modelled by an outward shift of the demand curve rather than a perverse demand curve.
You might also like
Price Mechanism (Revision Presentation)
Teaching PowerPoints
The Invisible Hand of the Ticket Tout
1st March 2015

Uber Surge Pricing and the Tube Strike
9th July 2015

Salmon Supply and Sushi
1st February 2016
Changes in Equilibrium Prices
Topic Videos

Understanding Prices - Why Hasselblad Cameras Are So Expensive
9th August 2021
