Study Notes
ASEAN
- Level:
- A-Level, IB
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
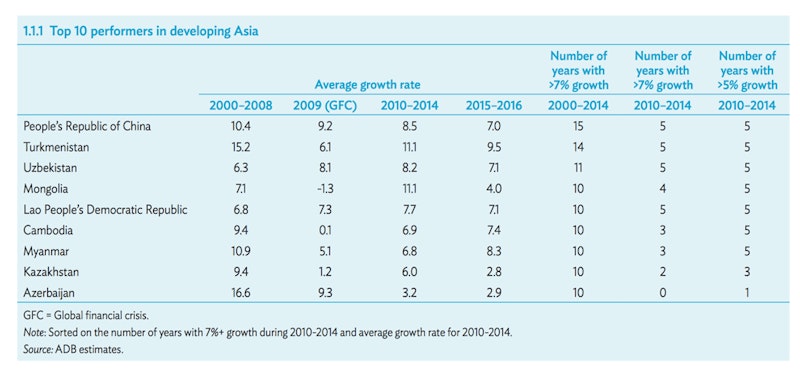
ASEAN is a trade bloc of 10 nations with an aggregate economic size of $2.3 trillion. The aim is to establish a fully-fledged economic community (AEC) by the end of 2015
The ASEAN trading bloc's diversity – ranging from advanced economies like Singapore to developing countries like Myanmar is an interesting and important feature – who will be the winners and losers from deeper economic integration in the region?
Current members;
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao P.D.R., Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam)
Economic Background to ASEAN
- ASEAN is a middle-income region but with big differences in per capita incomes
- Countries such as Singapore and Brunei enjoy a very high GDP per capita at around $49,000 and $39,000, respectively, on par with the top tier of developed-market economies.
- In contrast, Myanmar and Cambodia have a GDP per capita (PPP adjusted) of just below $900.
- The ASEAN region has a population of over 600 million, roughly half that of China's or India's and around 9% of the world's total
- ASEAN's combined GDP of USD 2.3 trillion in 2012 is around 30% the size of China's, roughly the same size as that of the UK and 25% larger than India's. ASEAN GDP =3% of the world's total
- 25% of ASEAN trade is intra-regional trade – the aim is to increase this as economic ties deepen and also for a rise in intra-regional FDI flows
- China has emerged as the No. 1 trading partner for ASEAN
- 5 “ASEAN+1" free-trade agreements have been signed, with China, Japan, Korea, India and Australia/New Zealand respectively
The basics of a single market / economic community
As part of the ASEAN integration plans, barriers to trade in goods and services will be brought down or kept to a minimum.
Flows of investment, capital and skilled labour will be facilitated and co-operation in sectors designated as priority integration sectors will be promoted.
- Free flow of goods and services
- Freer flow of capital and the Free flow of skilled labour
- Priority integration sectors
- Food, agriculture and forestry
This will be added to by establishing regional standards for competition policy, Consumer protection, Intellectual property rights, taxation and e-commerce
The ASEAN Infrastructure Fund was established with the Asian Development Bank to fund physical infrastructure projects in ASEAN. An example is the building of a new high speed railway between Malaysia and Singapore.
You might also like

A Tale of Two Financial Crises: the 1930s and Now
16th December 2014

Nissan invests £100m into the Sunderland plant
3rd September 2015

Realising One Market for Africa
16th July 2016
Relative size of major world economies
Topic Videos
Protectionism - Barriers to Trade (Quizlet Revision Activity)
Quizzes & Activities
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails