Topic updates
Examining Trade Dependency - Applied Examples

21st September 2022
We were discussing trade dependency in our Year 13 Economics class today and drew on real world data from countries such as Bangladesh, Zambia and Vietnam. I've linked to a short video of the key points from the session.
Benefits of exports for an emerging / developing country such as Bangladesh
- Exports generate funds to pay for imports
- Exports create jobs and can help lift per capita incomes which then reduces absolute poverty
- Exports are an injection into the circular flow which can have positive multiplier & accelerator effects
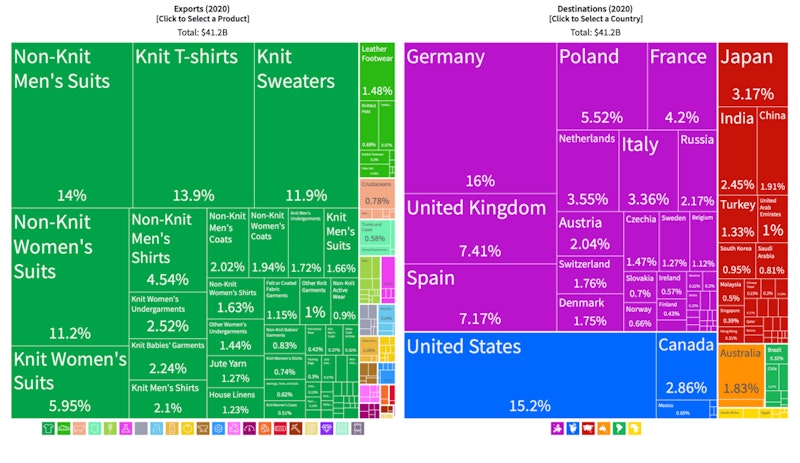
Risks/ downsides for emerging / developing countries who have a high trade dependency on a narrow range of products / export markets
- Makes an economy more vulnerable to external economic shocks and recessions in trade partners
- Country is more exposed to volatile global commodity prices – affecting trade balance / jobs
- Environmental aspects from over-production
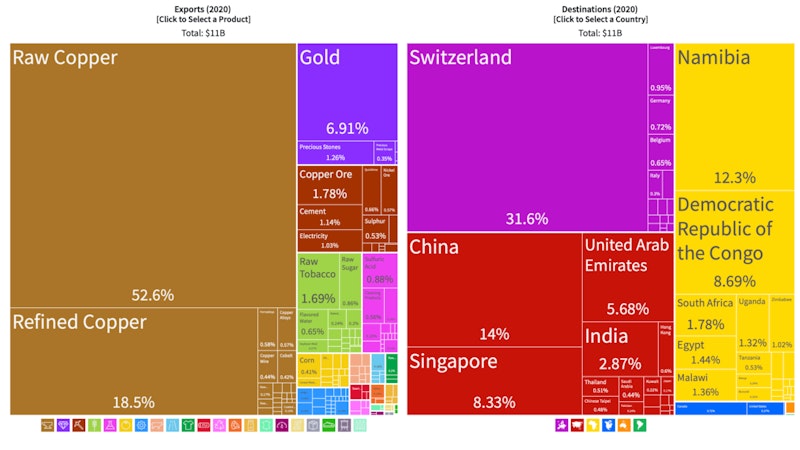
Strategies that a country might use to reduce trade dependence
- Investment in the human capital of the labour force – to increase / expand their capabilities
- Use foreign direct investment to broaden (diversify) a country’s industrial / export base
- Use of selective import controls to promote industrialisation / import substitution
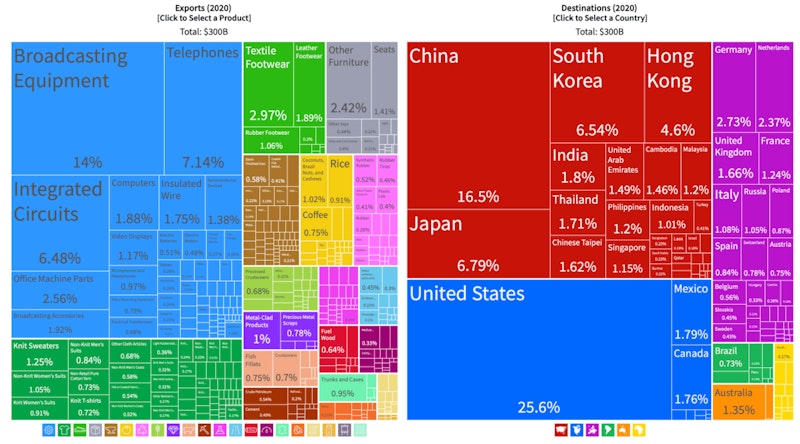
In this revision video we examine the extent to which countries are dependent on exporting a narrow range of products and to only a limited number of countries. Often, a high level of trade dependency can act as a barrier to sustainable growth and development.
You might also like

Sugar Cane and Economic Development in Mauritius
20th October 2014
Aggregate Demand - Revision Presentation
Teaching PowerPoints

Brexit: Britain's Major Export Products and Markets
9th March 2016
The Importance of Trade in Raw Materials
9th February 2017
Botswana must curb diamond reliance
4th February 2021

Brewed to Perfection or Priced Out? The Future of Tea
22nd July 2024