Study Notes
Revenue and Demand
- Level:
- AS, A-Level
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 14 Apr 2017
A business generates revenue by satisfying demand from customers. In other words, revenues flow from customer demand – but only if a business has a product that meets the customer needs and expectations.
What are revenue and demand
The terms revenue and demand are related, but different:
Revenue
Revenue is the amount (value) of a product that customers actually buy from a business
Demand
Demand is the amount of a product that customers are prepared to buy.
Demand can be measured in terms of volume (quantity bought) and/or value (£ value of sales)
Factors affecting the level of demand
Various factors will affect the level of demand:
- Prices & Incomes (you look at this in more detail when considering elasticity of demand)
- Tastes & fashions
- Competitor actions
- Social & demographic change
- Seasonal changes
- Changing technology
- Government decisions
The relationship between quantity demanded and price can be shown graphically by drawing a demand curve, as illustrated below:
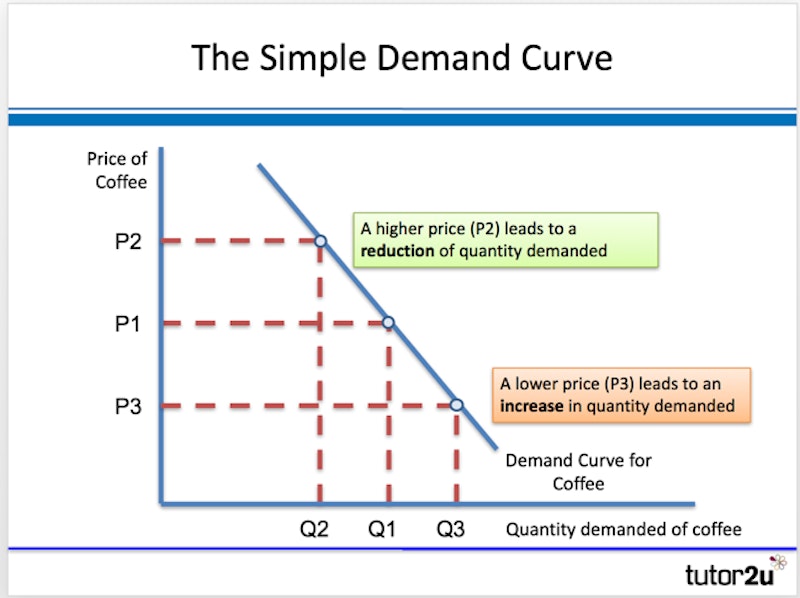
Revenue
There are various different names for the same thing – the value of what a business sells!
- Sales
- Revenues
- Income
- Turnover
- Takings
They all mean the same thing - revenue arises through the trading activities of a business.
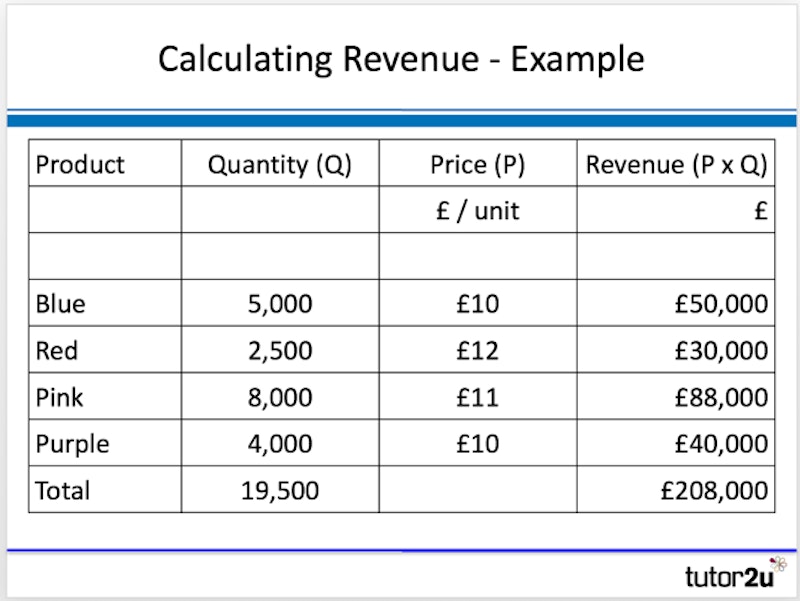
The value of revenue achieved in a given period is a function of the quantity of product sold multiplied by the price that customers paid. So revenues can be calculated using the following important formula:
Total revenue = volume sold x average selling price
An example of this calculation is shown in the table below:
The two ways to increase revenue
There are two main ways of increasing revenue:
Increase the quantity (amount) sold
- Perhaps by cutting the price or offering volume-related incentives (e.g. 2 for price of 1)
- Key issue - is demand sensitive to price? Will volumes demanded rise if the price is reduced and, if so, by enough to increase revenue? This is determined by the price elasticity of demand.
Achieve a higher selling price
- Best to add value rather than simply increase price
- Does market research suggest that prices are high enough or too low?
You might also like
Income Elasticity of Demand
Study Notes

The Demand/ Correlation Grid - Free Teaching Resource!
10th December 2015
Plants Help Give Pret's Sales a Boost!
21st April 2016
Business Maths - Calculating Percentage Changes
Topic Videos

Market Supply & Demand: Heavy Losses for New Zealand Dairy Farmers
12th August 2016
The External Environment: AQA A Level Business "Key Word Chop" Activity
Quizzes & Activities
Supply and demand for butter in France
1st November 2017

A Prime Example of Price Elasticity of Demand
26th July 2022
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails