Study Notes
Market Supply
- Level:
- AS, A-Level
- Board:
- Edexcel, OCR, IB
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
Supply is the quantity of a good or service that a producer is willing and able to supply onto the market at a given price in a given time period.
The Basic Law of Supply
The basic law of supply is that as the selling price of a product rises, so businesses expand supply to the market. The higher selling price acts as an incentive for businesses to produce more – and it may also attract other suppliers into the market.
This is illustrated in the diagram below:

Causes of Changes in Market Supply
The four main causes of changes in the amount supplied to a market are:
- Costs of Production
- External Shocks
- New Technology
- Taxation & Subsidies
Let’s look briefly at each of these
Supply and Costs of Production
It stands to reason that the costs of producing output will influence how much a business is able to supply:
- Lower unit costs mean that a business can supply more at each price – for example through higher productivity
- Higher unit costs cause an inward shift of supply e.g. a rise in wage rates or an increase in energy prices / other raw materials
For example, consider businesses that makes food products that contain a substantial amount of wheat. Falling wheat prices will cause a reduction in the resource costs for food manufacturers such as cereal producers. If other factors remain constant, producers who use wheat will be able to supply more for the same cost.

Supply and External Shocks
Significant and often unexpected changes in the external business environment usually impact on market supply.
For example, the sharp and sustained economic downturn between 2008-2012 across the world’s developed economies led to many firms cutting back the scale of their operations, including cutting production capacity.
The chart below shows how in 2009 (during the global economic recession) demand for sports shoes declined and Adidas responded by cutting output.

Supply and New Technology
Technological change encourages new entrants to a market (increasing supply) and can also enable existing suppliers to become more efficient, thereby increasing their potential to supply.
A good example is the 3D printing industry where the rapid development of additive manufacturing techniques has led to an explosion in supply of and demand for 3D printers.
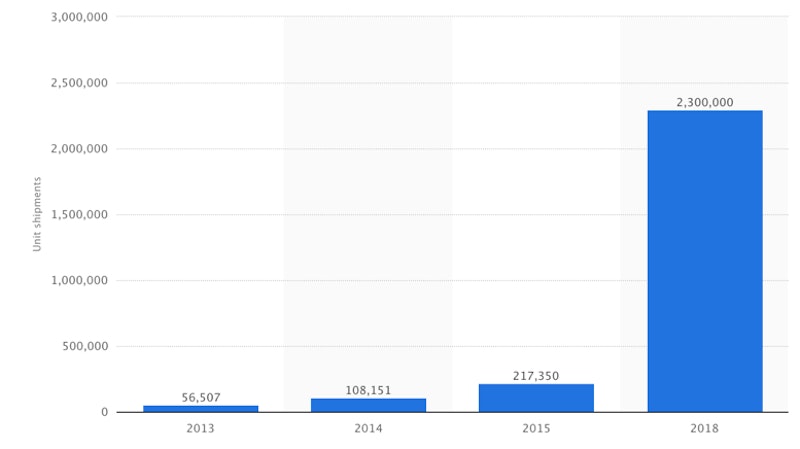
Supply and Taxation
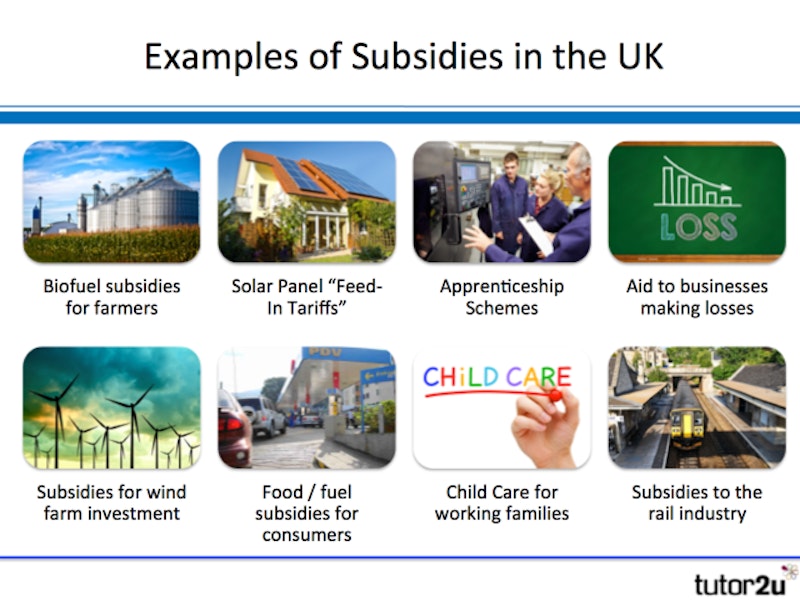
Changes in taxation can affect both supply and demand.
For example, the provision of subsidies to households and businesses installing solar panels in recent years encouraged a substantial increase in supply to the market.
You might also like
Working With Suppliers
Teaching PowerPoints

Supply and Demand: Bad News for Chocolate Lovers
6th August 2015

Solar Subsidies - Fears for the UK Solar Industry
6th September 2015
Market Equilibrium
Study Notes
Open Trade & Protectionism
Quizzes & Activities
Free-range egg market comes to the boil
2nd December 2016
The impacts of Budget 2017
9th March 2017

Butter Prices On The Rise - The Effect on Business Costs
14th September 2017
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails