Study Notes
External Environment: Taxation (GCSE)
- Level:
- GCSE
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
There are some key reasons why government needs to levy taxes; the main ones are:
- To raise revenue to finance government spending
- Managing aggregate demand - to help meet the government's economic objectives
- Changing the distribution of income and wealth
- Market failure and environmental targets – taxes may help correct market failures (e.g. pollution)
An important distinction can be made between direct and indirect taxes:
Direct taxation
Direct taxation is levied on income, wealth and profit
Direct taxes include:
Income Tax
National Insurance Contributions
Corporation Tax
Capital Gains Tax
Indirect taxation
Indirect taxes are levied on spending by consumers on goods and services
Examples:
VAT (currently 20% on relevant spending)
Excise duties on fuel and alcohol, car tax, betting tax and the TV licence
Who pays?
The burden of an indirect tax might be passed onto the consumer by the producer
Depends on the price elasticity of demand and supply for the product
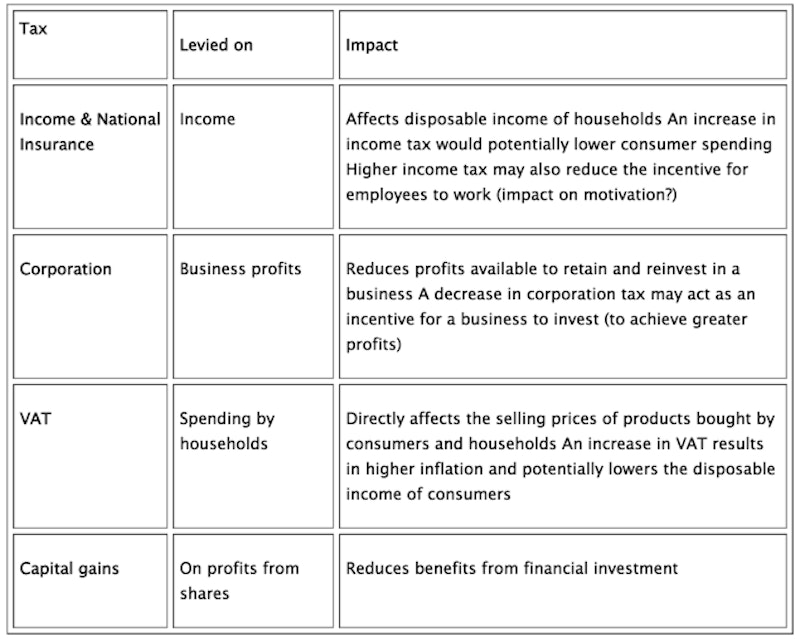
The effects of the main types of taxation on businesses (in the UK) can be summarised as follows:
You might also like
Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Study Notes
Fiscal & Monetary Policy
Quizzes & Activities

Tax Avoidance and the Diverted Profits Tax
25th May 2015

Understanding the Economy: Govt Budget Deficit and Debt
11th December 2015
The impacts of Budget 2017
9th March 2017
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails