Study Notes
External Environment: Exchange Rates (GCSE)
- Level:
- GCSE
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
An exchange rate is the value of one currency expressed in terms of another.
So £1 may be worth $1.55 and €1.33.
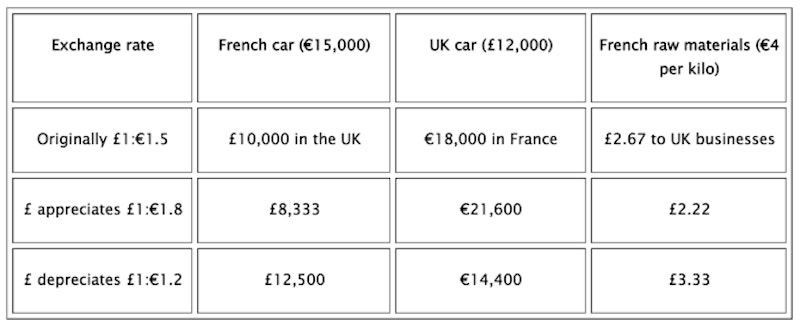
- A currency that is getting stronger or appreciating is a currency that is going up in value against another. So £1:$1.5 moving to £1:$1.8 means the pound is getting stronger
- A currency that is becoming weaker or depreciating is a currency that is going down in value against another. So £1:$1.8 moving to £1:$1.5 means the pound is getting weaker
Currencies change in value against each other all the time. This is because most currencies are based on flexible exchange rates. The notable difference is in the Euro zone (see below).
Currencies change in value because there is a change in demand for holding that currency. Households, governments and businesses need other countries currencies to buy their goods and services (e.g. holiday makers for purchasing wine or a business buying spare parts for machinery from France will need Euros).
A change in exchange rates might affect a business in the following ways:
- Exchange rates changes can increase or lower the price of a product sold abroad
- The price of imported raw materials may change
- The price of competitors' products may change in the home market
For example an increase in the exchange rate will mean that price abroad goes up, lowering sales; price of imported raw materials falls, either leading to a fall in price and more sales, or an increase in profits; competitors' prices fall, meaning lower sales.
You might also like

Exchange Rates, Costs and Competitiveness - Making the Link
10th March 2015
Exchange Rates
Quizzes & Activities
SWOTting Staycations
21st December 2016
Kraft withdraw their mega-takover offer
19th February 2017

Economic Environment | Exchange Rates - the Pound Gets Weaker and Weaker
25th September 2022
Daily Email Updates
Subscribe to our daily digest and get the day’s content delivered fresh to your inbox every morning at 7am.
Signup for emails