Study Notes
Urbanisation and Migration
- Level:
- A-Level, IB, BTEC National
- Board:
- AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC
Last updated 9 Aug 2019
Businesses need to consider key changes in population as they determine their strategy. Two aspects to consider are urbanisation and migration.
Urbanisation
Urbanisation is:
The movement of people within a country from the countryside to urban areas (towns and cities)
Degree of urbanisation: usually measured by the percentage of the population living in urban areas
Migration
Migration is:
The movement of people between countries or regions
Immigration - the movement of people into a country
Emigration – movement of people out of a country
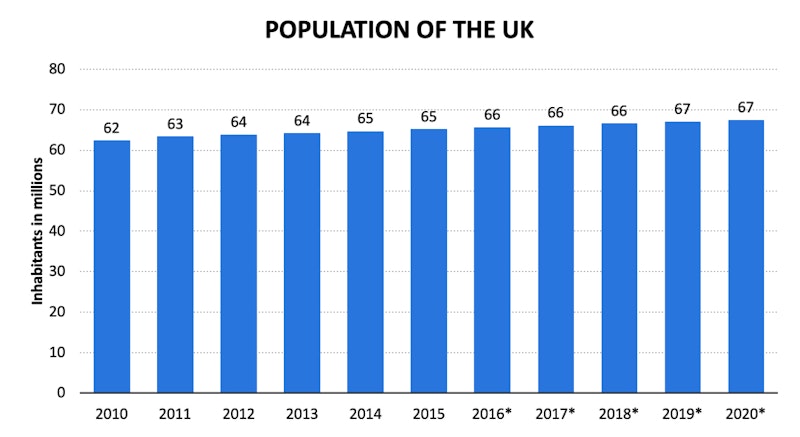
Example Urbanisation & Migration Data: UK
The UK is a good example of the typical levels of urbanisation and migration for a developed economy. The key features of the UK are:
- Steady growth in population
- Significant net inward migration in recent years
- Slow growth in degree of urbanisation

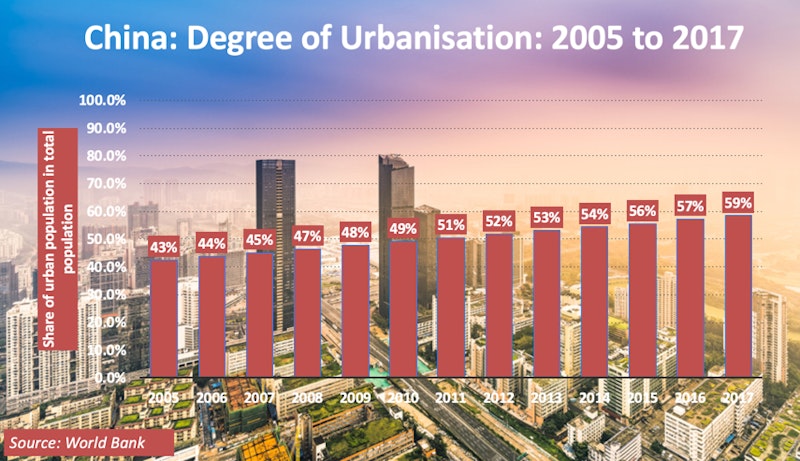
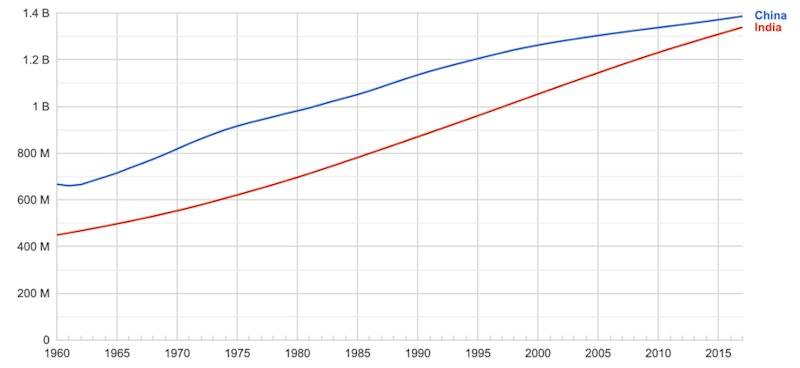
Example Urbanisation & Migration Data: China
By contrast, the population of fast-growing economies like China and India has surged ahead in recent decades.
China in particular has supported its population growth with a mass urbanisation programme.

Business Implications of Changes in Urbanisation and Migration
Some key business implications of changes in the level of population and extent of urbanisation include:
Rising population = higher demand for goods and services
More urbanisation (particularly emerging economies) = more affluent “middle class” consumers
Impact of net inward migration on public services (pressure on government spending), but helps economy to grow + businesses have larger supply of labour
You might also like

BUSS4 Manufacturing: Research Bullet 4 - Location
15th June 2015

Emerging Markets Are the Target for Global Tobacco Giants
19th July 2017

How the Global Economy is Changing
3rd August 2017

Multinationals, Emerging Economies and the Obesity Epidemic
19th September 2017
Why is there a shortage of workers in agriculture?
14th November 2017